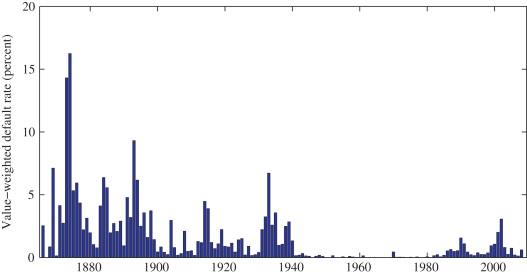
In the labyrinthine world of corporate finance, where fortunes are made and lost in the blink of an eye, a new specter looms large—corporate defaults. As global markets grapple with unprecedented challenges, the risk of companies failing to meet their financial obligations is no longer a distant thundercloud but a storm on the horizon. This growing threat, fueled by economic uncertainties and shifting financial landscapes, demands our attention and understanding. In this article, we delve into the intricate dynamics of corporate defaults, unraveling the complex web of factors that contribute to this escalating risk. With an authoritative lens, we explore what this means for investors, businesses, and the global economy at large, equipping you with the knowledge to navigate these turbulent waters. Welcome to a world where financial vigilance is not just prudent but essential.
Understanding the Economic Triggers Behind Rising Defaults
The intricate dance of economic factors often sets the stage for rising corporate defaults, weaving a complex tapestry of financial stress. At the forefront, interest rate hikes play a pivotal role. As central banks tighten monetary policy to curb inflation, borrowing costs soar, squeezing profit margins and stretching balance sheets. Companies, particularly those heavily reliant on debt, find themselves grappling with increased interest expenses, which can lead to liquidity crunches and eventual defaults.
Moreover, global supply chain disruptions have become a persistent thorn in the side of many industries. The pandemic-induced chaos, coupled with geopolitical tensions, has led to erratic supply chains, driving up costs and causing delays. Businesses struggling to manage these disruptions face dwindling cash reserves, making it challenging to meet financial obligations. Additional triggers include:
- Weak consumer demand: A sluggish economic recovery can dampen consumer spending, affecting revenue streams.
- Currency fluctuations: Volatile exchange rates can impact companies with significant international exposure.
- Regulatory changes: New policies and compliance requirements can impose unexpected financial burdens.
Understanding these triggers is crucial for stakeholders aiming to navigate the turbulent waters of corporate finance, ensuring preparedness in the face of mounting default risks.

Analyzing Sector Vulnerabilities and High-Risk Industries
In the intricate web of the global economy, certain sectors stand out as particularly susceptible to financial distress, posing significant risks for corporate defaults. High-risk industries often share common characteristics that make them vulnerable to economic fluctuations and market volatility. These include sectors heavily reliant on commodity prices, such as oil and gas, where market shifts can rapidly erode profit margins. Additionally, industries with high levels of debt, like telecommunications and utilities, face mounting pressure as interest rates rise, making refinancing a daunting challenge.
Moreover, sectors grappling with technological disruption are at a heightened risk. Traditional retail, for instance, is continually threatened by the e-commerce juggernaut, forcing companies to innovate or perish. Similarly, the automotive industry is navigating the seismic shift towards electric vehicles, with legacy manufacturers struggling to adapt. In this landscape, businesses must remain agile, continuously reassessing their strategies to mitigate these vulnerabilities. Key indicators to watch include:
- Debt-to-equity ratios that highlight financial leverage.
- Profit margin trends that reflect operational efficiency.
- Market share fluctuations that indicate competitive positioning.
By understanding these dynamics, stakeholders can better anticipate and navigate the challenges posed by high-risk industries.

Strategies for Investors to Mitigate Default Risks
Investors seeking to shield their portfolios from the looming threat of corporate defaults can employ a variety of strategic measures. First and foremost, diversification remains a cornerstone strategy. By spreading investments across different sectors and geographies, investors can reduce the impact of a default in any single area. Additionally, consider focusing on high-quality bonds and blue-chip stocks that have a proven track record of weathering economic downturns.
- Conduct Thorough Due Diligence: Analyze the financial health of companies, paying close attention to their debt levels, cash flow, and earnings stability.
- Monitor Economic Indicators: Keep an eye on interest rates, inflation, and other macroeconomic factors that could signal increased default risks.
- Utilize Credit Ratings: While not infallible, credit ratings can provide insights into a company’s default risk. Consider favoring investments with higher ratings.
- Incorporate Hedging Strategies: Options, credit default swaps, and other financial instruments can help mitigate potential losses from defaults.
By implementing these strategies, investors can better navigate the turbulent waters of today’s financial landscape, minimizing potential losses and safeguarding their investments against the rising tide of corporate defaults.
Proactive Measures for Companies to Strengthen Financial Resilience
In an era marked by economic volatility, companies must adopt a proactive stance to safeguard their financial stability. Implementing robust strategies can significantly mitigate the risk of corporate defaults. Here are some critical measures businesses can take:
- Enhance Liquidity Management: Regularly assess cash flow projections and maintain a healthy cash reserve to cushion against unexpected downturns.
- Diversify Revenue Streams: Explore new markets and products to reduce dependency on a single source of income, thereby spreading risk.
- Strengthen Credit Policies: Implement stringent credit assessments and establish clear terms to minimize exposure to bad debts.
- Optimize Operational Efficiency: Conduct regular audits to identify and eliminate inefficiencies, ensuring that resources are utilized effectively.
- Invest in Risk Management: Develop comprehensive risk management frameworks that anticipate potential threats and devise contingency plans.
By embedding these strategies into their core operations, companies can not only withstand financial pressures but also position themselves for sustainable growth in an unpredictable economic landscape.